September 1, 2025 | 03:48 GMT +7
September 1, 2025 | 03:48 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
September 1, 2025 | 03:48 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Arcording to Producereport, recently, the General Administration of Customs of China issued an announcement outlining the phytosanitary requirements for importing fresh pineapples from Sri Lanka.
Pineapples are the second fruit from Sri Lanka to gain market access to China, following bananas, which were granted approval in 2015.
The most common pineapple variety in Sri Lanka is the Mauritius (“Queen”) pineapple. This fruit is known for its conical shape, spiny leaves and golden yellow flesh, and its rich aroma and sweet taste make it ideal for fresh consumption.

Pineapples are the second fruit from Sri Lanka to gain market access to China. Photo: Producereport.
Despite Sri Lanka having over 100 kinds of edible fruits, the local agricultural sector is underdeveloped, resulting in significant post-harvest losses, low yields and a failure to meet international quality standards.
Although Sri Lankan bananas were approved for export to China almost a decade ago, actual shipments remain almost nonexistent.
Welly Soegiono, PT Great Giant Pineapple (GGP)’s director of corporate affairs - a large private-label manufacturer of canned pineapples said: “Since China's domestic production of pineapples is very limited, there is huge potential for imported pineapples".
In May 2023, the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization’s South - South Cooperation program launched a new project in Sri Lanka with a budget of USD 1.5 million.
The initiative aims to improve the production and commercialization of Sri Lankan fruit value chains, enhance fruit quality, and increase the sector’s market value. Over the course of two and a half years, the project will be implemented across five regions in Sri Lanka, focusing on improving the production, yield and commercialization of three important local fruit crops: bananas, mangos and pineapples.
The GACC announcement details the quarantine pests of concern, which include the giant African snail (Lissachatina fulica), cotton thrips (Frankliniella schultzei), papaya mealybug (Paracoccus marginatus), obscure mealybug (Pseudococcus viburni), brown soft scale (Coccus hesperidum), cockspur grass (Echinochloa crus-galli), East African couchgrass (Digitaria abyssinica), tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus and Dickeya dadantii, a bacterium responsible for soft rot.
According to the phytosanitary protocol, orchards intending to export fresh pineapples to China are required to establish a comprehensive quality management and traceability system under Sri Lankan supervision as well as implementing good agricultural practices and integrated pest management techniques.
During the packaging process, procedures such as manual sorting, screening, scrubbing or high-pressure water jet cleaning must be used to ensure that the fruits and crowns are free from potential contaminants such as insects, mites, snails, rot, grass seeds, plant residues and soil.
In the first two years after the commencement of trade, Sri Lankan authorities are required to take samples of each shipment, inspecting no less than 2% of each batch. If no phytosanitary issues arise within this two-year period, the sampling proportion may be reduced to 1%. However, if any quarantine pests of concern are detected, the entire batch may not be exported to China.
Moreover, depending on the situation, the relevant orchards and packaging plants could be suspended from exporting pineapples to China for the remainder of the export season.
Sri Lankan authorities must also make efforts to identify the underlying causes and take effective measures, as well as maintaining records and providing them to Chinese authorities upon request.
At present, there are about 90 countries and regions worldwide where pineapples are cultivated. The total global area of pineapple cultivation exceeds 400,000 hectares and is mainly distributed in Asia, America, and Africa.
The top 10 pineapple producers are Thailand, the Philippines, China, Brazil, India, Nigeria, Costa Rica, Mexico, Indonesia, and Kenya, and their production accounts for approximately 73% of the global total pineapple output.
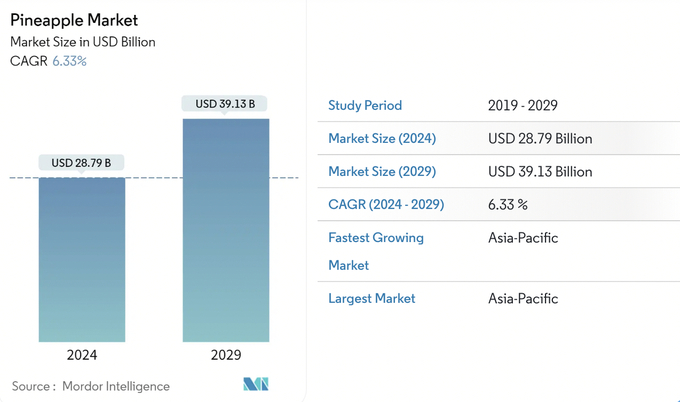
The global pineapple market is gradually expanding significantly, with showing growth from USD 27.08 billion in 2023 to USD 28.7 billion in 2024, estimated to reach USD 36.8 billion in 2028 and USD 39.13 billion by 2029, growing at a CAGR of 6.33% during the forecast period (2024 - 2029). Among them, Asia - Pacific is the greatest potential market.
In 2021, Costa Rica, Indonesia, and the Philippines were the top three pineapple producers worldwide. Costa Rica produced 2.9 million metric tons of pineapples in 2021. These countries produce the fruit primarily for fresh fruit markets and the processing.
The demand for pineapples has been growing in recent years. In Asia, the countries with the highest volumes of pineapple consumption in 2018 were the Philippines 2.3 million tonnes, Thailand 2.1 million tonnes and Indonesia 1.8 milion tonnes, with a combined 53% share of total consumption. These countries were followed by India, China, Viet Nam and Taiwan, which together accounted for a further 38%.
In value terms, the largest pineapple markets in Asia were Thailand (3 billion USD, China USD 2.2 billion and the Philippines USD 1.9 billion with a combined 59% share of the total market. These countries were followed by India, Indonesia, Viet Nam and Taiwan, Chinese, which together accounted for a further 34%.
Asia is the largest region in the world both in terms of production and consumption. This is due to large local consumption and the highest area under pineapple production. In 2021, Indonesia is the top producer in the region with 2.88 million metric ton in 2021, followed by the Philippines with 2.86 million metric ton and India with 1.7 million metric ton.Indonesia is promoting pineapple exports to the Chinese market. In August 2022, the General Administration of Customs of China issued a new protocol, which approved the export of Indonesian fresh pineapples to China if they meet certain requirements.
Welly Soegiono, PT Great Giant Pineapple (GGP)’s director of corporate affairs - a large private-label manufacturer of canned pineapples said: “Right after Indonesian fresh pineapples gained official access to the Chinese market, we started to plant more pineapple trees to boost our production capability”.
“Since China's domestic production of pineapples is very limited, there is huge potential for imported pineapples", said Soegiono.
The total extent of pineapple in Sri Lanka is about 4,750 hectares producing a total of 35,000 mt/year, 70% of which is produced in the Kurunegala and Gampaha districts. Meanwhile, Vietnam's pineapple output in 2022 will reach 705,000 tons, with total pineapple export turnover of USD 673 million.
Vietnamese pineapple production is anticipated to reach 807,000 metric tons by 2026. This is up from 726,000 metric tons in 2021, a growth rate of 1.8% year on year on average. Since 1966, Vietnamese supply has increased 5.5% year on year.
However, Mr. Ngo Xuan Nam, Deputy Director of the SPS Vietnam Office, said that currently Vietnamese pineapples are not officially exported to the Chinese market.
The pineapple market has immense opportunities owing to the demand for the product, increased awareness among consumers, and growth in investments from private investors and companies.At the same time, pineapple consumption demand not only in China but globally is forecast to increase because
Beside this, the rising demand for food extracts that add nutritional value while providing a tangy flavor and the growing popularity of pineapple flavor in China and over all the world are expected to drive the growth of the market. Furthermore, pineapple products such as pineapple powder has a longer shelf life and used in various food and beverages sector, pharmaceuticals are expected to drive the market growth. This will be an opportunity for pineapple producing and exporting countries, including Vietnam has promoted exports, expanded markets, and reaped success from “sweet fruits”.
The total extent of pineapple in Sri Lanka is about 4,750 hectares producing a total of 35,000 mt/year, 70% of which is produced in the Kurunegala and Gampaha districts. Meanwhile, Vietnam's pineapple output in 2022 will reach 705,000 tons, with total pineapple export turnover of USD 673 million. Vietnam’s pineapple production is anticipated to reach 807,000 metric tons by 2026.
Translated by Hong Tham

(VAN) Vinod Ahuja, FAO Representative in Viet Nam, affirms that Vietnam's success lies not only in its abundant national reserves but also in increasingly diversified value chains and enhanced competitiveness.

(VAN) Vietnamese engineers have mastered technology, successfully manufacturing an automatic system for environmental agricultural monitoring and measurement, aiming at the dream of 'robotization'.

(VAN) Over the past 80 years, the food sector has walked alongside the nation, from shared jars of rice during the resistance to ships carrying Vietnamese rice brands across the five continents.

(VAN) Vietnam’s geology sector has marked its presence through achievements in mineral surveying and exploration, affirming the country’s resource potential and contributing to sustainable development.

(VAN) The Viet Nam Institute of Meteorology, Hydrology and Climate Change Director shares insights on 80 years of the sector’s achievements, its role in disaster forecasting, and messages for the younger generation.

(VAN) VAN News cordially introduces the message from Mariam J. Sherman - World Bank Division Director for Viet Nam, Cambodia and Laos - about the Viet Nam's 80-year journey of development.

(VAN) That is the theme of the 2025 International Workshop “2nd International Conference on Biological Protection in Sustainable Agriculture (ICBPSA),” held in Hue City.