August 1, 2025 | 13:49 GMT +7
August 1, 2025 | 13:49 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
August 1, 2025 | 13:49 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Vietnam's bilateral trade turnover with India in 2024 was roughly 15 billion USD, a 4.5% increase from 2023, according to the General Custom of Vietnam.
In that year, Vietnam's exports to India totaled 9.06 billion USD, a 7.6% increase from the previous year. Conversely, India's imports to Vietnam totaled roughly 5.83 billion USD, a 0.6% decrease.

Bilateral trade turnover between Vietnam and India in 2024 will reach nearly 15 billion USD, an increase of 4.5% compared to 2023. Photo: Duy Hoc.
Vietnam maintains its superior trade surplus advantage in its trade with India, which is attributable to the expansion of its primary export products.
In the export structure, mobile devices of all types and specifications accounted for 17.5% of the total export turnover, with a turnover of 1.68 billion USD, a minor increase of 4.5%. The turnover of computer and electric products and details is 1.5 billion USD, which accounts for 15.6% of the proportion. This places them in the second position. The turnover of machine, equipment, and appliance was USD 947 million, which accounted for 9.8% of the proportion.This demonstrates the necessity of stabilizing the Indian market for Vietnam's industrial products.
It is worth noting that various other export groups in Vietnam experienced substantial growth in 2024. For example, tea increased by 18.7%, wood and wood products rose by 18%, seafood products increased by 12%, bamboo, rattan, and sedge products increased by 11%, rubber products, confectionery, and cereals all increased by 11%, plastic products grew by 10.4%, various textile fibers increased by 10%, textiles and garments by 9.5%, and chemical products and chemicals increased by 9.5%.
It is evident that Vietnam continues to increase its share of the commodity industry sector in India. The agricultural sector experienced an 18% increase in wood and wood products, which amounted to 212.57 million USD. Pepper, tea, and seafood products all experienced positive development, indicating the high demand from the Indian market.
In order to increase their market share, businesses must implement more effective market penetration strategies, as Vietnam's coffee exports remained consistent at USD 38.83 million. Vietnam's exports to India are characterized by a growth in sectoral diversification, with a particular emphasis on high-tech products and agricultural commodities, which continue to be critical areas of focus.
The trade structure between the two nations is highly complementary, which promotes sustainable economic cooperation. India is a source of essential raw materials and finished products for Vietnam, such as steel, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, textiles, animal feed, and fisheries, which helps to support domestic industrial growth.
In contrast, Vietnam must further capitalize on its market potential in India, with a particular emphasis on electronics, textiles, processed foods, light industries, and agricultural products like coffee, pepper, and seasonings.
In contrast, Vietnam's imports from India during this period totaled USD 5.83 billion, which represents a 0.6% decline from the same period in 2023. India's imports comprised only 1.55% of Vietnam's total import turnover. Vietnam's trade surplus with India in 2024 was USD 3.2 billion, a 22.2% increase from 2023.
Translated by Linh Linh

(VAN) OCOP products from Quang Ninh are gradually reaching international markets, with a focus on nationally certified 5-star products.

(VAN) After a sharp decline in the early months of the year, Vietnam's durian exports are experiencing a strong recovery, driving the overall rebound in fruit and vegetable exports.

(VAN) The volume of durians imported through Guangxi has surged as the region invests in logistics infrastructure and takes advantage of tariff incentives from the RCEP agreement between China and ASEAN.
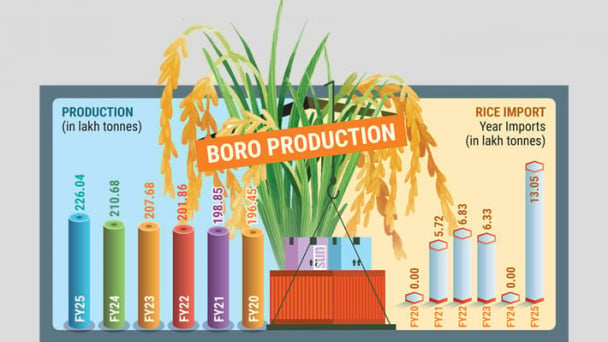
(VAN) Rice prices in Bangladesh have shot up over the past year, rising by as much as 16%, despite a record-breaking harvest this season and large volumes of imports in 2024-25 fiscal year.

(VAN) U.S. seafood tariffs trigger major disruptions in global supply chains. Vietnam proactively shifts markets and strengthens internal capacity to maintain its export position.
/2025/07/26/1437-0-nongnghiep-221433.jpg)
(VAN) To achieve successful exports, Vietnamese agricultural products must tell a product story that aligns with current trends and reaches to the needs and emotions of international consumers.

(VAN) Over 600,000 Vietnamese coffee farming households face major challenges as the EU tightens traceability and anti-deforestation requirements by the end of 2025.