November 27, 2025 | 21:20 GMT +7
November 27, 2025 | 21:20 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
November 27, 2025 | 21:20 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
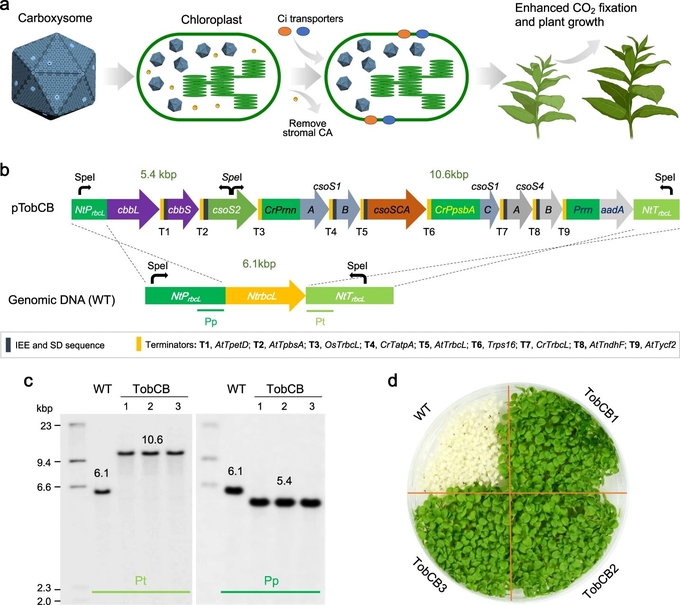
Synthetic engineering of α-carboxysomes into tobacco chloroplasts. a Schematic representation of the strategies of introducing carboxysomes and bicarbonate transporters into plant chloroplasts and eliminating chloroplastic CA to install a complete CCM for enhanced photosynthetic carbon fixation and plant yields. b Gene organization of α-carboxysome-expressing construct for tobacco chloroplast expression and the rbcL locus in the wild-type (WT) tobacco chloroplast genome. The α-carboxysome-expressing construct contains nine genes coding Rubisco (cbbL and cbbS), the linker protein CsoS2 (csoS2), carbonic anhydrase (csoSCA), shell hexamers (CsoS1A/B/C) and pentameric proteins (csoS4A/B). The genes were grouped into three operons driven by NtPrbcL (native promoter of rbcL in Nicotiana tabacum), CrPrrn (promoter of ribosomal RNA in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii), and CrPpsbA (promoter of psbA in C. reinhardtii), respectively. The Streptomycin/Spectinomycin adenylyltransferase gene (aadA) was driven by the tobacco plastid rRNA operon promoter (Prrn)73. Intercistronic Expression Elements (IEE), SD (Shine-Dalgarno) sequence, and Terminators (T) were listed. At, Os, and Cr indicate Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, and C. reinhardtii, respectively. c, d Southern blot analysis (c) and seed germination (d) verified the successful transgene integration and homoplasmy of the three transplastomic plants obtained. The genomic DNA was digested by SpeI and hybridized with Digoxygenin-labeled probes of the promoter (Pp) and terminator (Pt) of rbcL in N. tabacum as indicated in (b). Seed germination was performed on Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium containing 500 mg L–1 spectinomycin. Source data are provided as a Source Data file. Credit: Nature Communications (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-37490-0
With global levels of carbon dioxide (CO2) rising and the population set to reach almost 10 billion by 2050, Professor Luning Liu's team of researchers used synthetic biology and plant engineering techniques to improve photosynthesis, creating a template that can be used on a mass scale.
Photosynthesis is the process by which plants use atmospheric CO2 to create nutrients, which are crucial for growth and the global ecosystem. The newly published paper details how the team of scientists have improved Rubisco, a key enzyme present in photosynthesis that converts CO2 into energy. Usually Rubisco is inefficient and limits photosynthesis in major crops. However, many microorganisms including bacteria have evolved efficient systems, named "CO2-concentrating mechanisms," to improve Rubisco.
Inspired by nature, the team has successfully engineered a catalytically faster Rubisco taken from bacteria, into tobacco plant cells that undertake photosynthesis to support plant growth. The new method improves the Rubisco's stability and ability to convert CO2 into energy, allowing plants to further thrive. The changes to the enzyme also potentially increase the plants ability to absorb CO2, helping to support the global effort to address climate change.
Professor Luning Liu, Department of Biochemistry and Systems Biology, University of Liverpool said, "We are extremely excited with this breakthrough. Overall, our findings provide proof-of-concept for a route to improving crop development and production that can withstand changing climates and meet the growing food requirements of the world's expanding population."
This latest study follows the team's recent attempt to engineer the faster Rubisco from bacteria to support plant growth.
(Phys.org)

(VAN) A new study reveals how the simultaneous effects of ocean acidification, salinity and loss of oxygen are making the world more fragile.

(VAN) Hopes are growing that the creation of the first 3D turkey gut model could be a turning point in the battle against the virulent blackhead disease.

(VAN) Tyson, America’s biggest meat supplier, plans to shutter one of its largest beef processing plants as the industry continues to struggle with low cattle supplies and political pressure from Washington.

(VAN) New FAO study shows how digital solutions are empowering farmers and fishers to prevent losses and build resilient agrifood systems.

(VAN) Brazil's COP30 presidency pushed through a compromise climate deal on Saturday that would boost finance for poor nations coping with global warming but that omitted any mention of the fossil fuels driving it.

(VAN) Poultry farmers in the UK have been warned that they could face one of the worst winters yet for bird flu.

(VAN) Prices of main-crop paddy have risen sharply, with jasmine rice hitting 16,100 baht per tonne — the highest level in years.