November 28, 2025 | 02:55 GMT +7
November 28, 2025 | 02:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
November 28, 2025 | 02:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
The satellite image above of an area of Turkey processed by the NASA Earth Observatory shows much of the farmland is white because it is covered by plastic. NASA says South Korea, Spain, and Turkey all use significant amounts of plastic to produce food in greenhouses. In China, plastic-covered greenhouses make up about three percent of the farmland.
The area around Almería, Spain has the largest concentration of greenhouses in the world. The greenhouses span over 64,000 acres (260 sq km) and have been around for decades.
The shift to greenhouses was dubbed the “White Revolution” in South Korea and allowed the country to grow fresh vegetables year round. Now, it’s helped grow exports and stabilize prices (pdf).
The amount of plastic in the world is incomprehensible. Carbon emissions from plastic is estimated to outpace coal emissions by 2030. A recent report (pdf) by FAO forecasts a 50% increase in demand by 2030 of plastics used in agriculture.
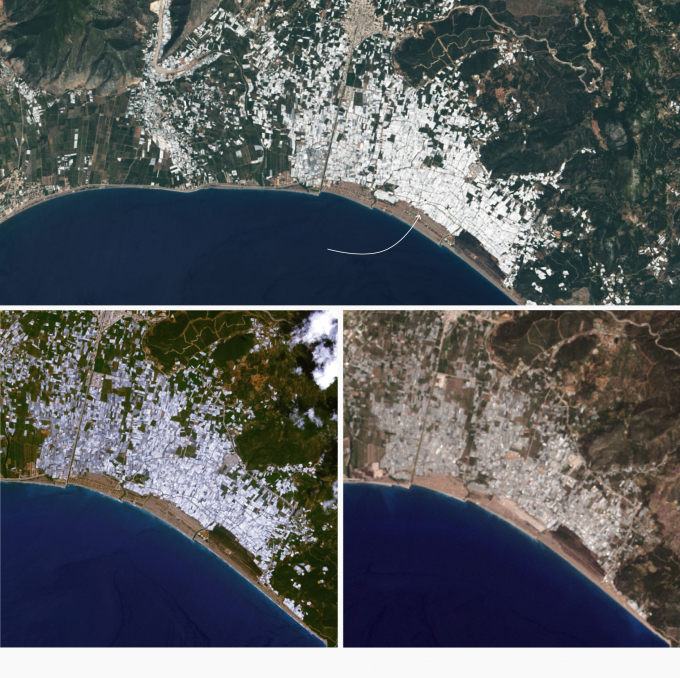
Data: USGS, NASA
Plasticulture and microplastics are ruining farmland
Plastic has found its way into many farming applications that have become integral to the industry. Relying on plastic in agriculture is derided as “plasticulture”. Plastic is cheap and makes tasks faster and lighter. Plastic film is used as a ground cover to prevent weed growth, and plastic containers trap moisture.
Plastic may have worthy benefits in the short term, but the long-term effects of using plastic each season cannot be ignored.
In particular, plastic films break down into microplastics, contaminating the soil. Only about 5% of plastic film is recycled according to Judith Enck, founder of Beyond Plastics and a former EPA regional administrator. Plastic films last for a season before they become unusable, as well as unrecyclable—leading to more single-use plastic each year. “We really need to look for non-plastic alternatives,” said Enck.
How does soil pollution affect plants?
Over time, plastic breaks down. When it’s smaller than five millimeters, it’s considered a microplastic. Nanoparticles of microplastics can enter the food chain. Studies already show microplastics are in air, water, and even human blood.
Chemicals in plastic can leach toxins into the soil particularly if the plastic is heated, exposed to sunlight for long periods, or worn-down. Plastic in soil can increase the pH and lower the microbial activity that keeps soil healthy and nutrient-rich.
Biodegradable alternatives to plastic in agriculture and gardening
There is little research exploring natural alternatives to ground-covering films and greenhouses covers. The results from using biodegradable mulch vary depending on the crop being grown and environmental conditions specific to a field. “Everything is extremely variable,” said Judith Conroy, a researcher at Coventry University in the UK.
Conroy is part of an effort in Europe to find agricultural plastic alternatives. Current options include corn and potato starches, and paper. But just because a material is biodegradable does not mean it’s sustainable.
There are few regulations on the use of plastic. “In order to be competitive with the farm up the road they kind of have no other choice,” said Conroy. “It sounds harsh to ban things, but you might well be making it more fair.”

In agriculture, plastic products greatly help productivity. Photo: FAO.org
In agriculture, plastic products greatly help productivity, such as in covering soil to reduce weeds; nets to protect and boost plant growth, extend cropping seasons and increase yields; and tree guards, which protect seedlings and saplings from animals and help provide a growth-enhancing microclimate. However, of the estimated 6.3 billion tonnes of plastics produced before 2015, almost 80 per cent had never been properly disposed of.
While the effects of large plastic items on marine fauna have been well documented, the impacts unleashed during their disintegration, potentially affect entire ecosystems.
And microplastics – less than 5 mm in size – have been found in human feces and placentas as well as been transmitted to fetuses through their pregnant mothers.
While most scientific research on plastics pollution has been directed at aquatic ecosystems, FAO experts say agricultural soils are thought to receive far greater quantities of microplastics.
Since 93 per cent of global agricultural activities occur on land, further investigation in this area is needed, according to the UN agency.
“This report serves as a loud call to coordinated and decisive action to facilitate good management practices and curb the disastrous use of plastics across the agricultural sectors”, said the FAO deputy chief.
(QZ; FAO.org)

(VAN) A new study reveals how the simultaneous effects of ocean acidification, salinity and loss of oxygen are making the world more fragile.

(VAN) Hopes are growing that the creation of the first 3D turkey gut model could be a turning point in the battle against the virulent blackhead disease.

(VAN) Tyson, America’s biggest meat supplier, plans to shutter one of its largest beef processing plants as the industry continues to struggle with low cattle supplies and political pressure from Washington.

(VAN) New FAO study shows how digital solutions are empowering farmers and fishers to prevent losses and build resilient agrifood systems.

(VAN) Brazil's COP30 presidency pushed through a compromise climate deal on Saturday that would boost finance for poor nations coping with global warming but that omitted any mention of the fossil fuels driving it.

(VAN) Poultry farmers in the UK have been warned that they could face one of the worst winters yet for bird flu.

(VAN) Prices of main-crop paddy have risen sharply, with jasmine rice hitting 16,100 baht per tonne — the highest level in years.