July 30, 2025 | 05:47 GMT +7
July 30, 2025 | 05:47 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
July 30, 2025 | 05:47 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
Graphical abstract. Source: DOI
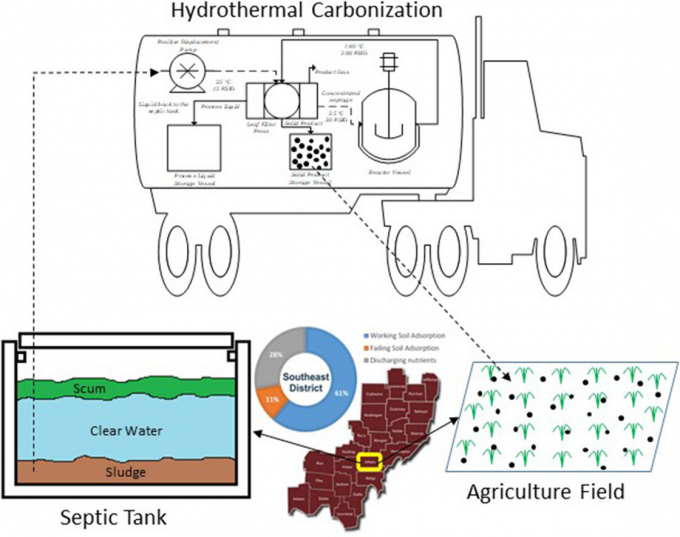
Biomedical and chemical engineering and sciences professor Toufiq Reza, along with former Florida Tech researchers Nepu Saha and Kyle McGaughy and Ohio University's Sarah Davis, released a new paper, "Assessing hydrothermal carbonization as sustainable home sewage management for rural counties: A case study from Appalachian Ohio" published in August in the journal Science of the Total Environment.
The major findings from the paper are that hydrothermal treatment of septic tank waste—known as septage—is economically viable and that this treatment could reduce the cost of pumping out septage by as much as 25 percent. Converting the waste to usable fertilizer could also significantly reduce the fertilizer demand of the study area, which for this research was rural Athens County, Ohio, a rural Appalachian county in the southeastern part of the state. This work also may have major impacts in developing countries, a benefit that underpins some of Reza's previous research.
For this study, waste is converted into fertilizer through a high temperature, high-pressure process called hydrothermal carbonization (HTC). HTC is a thermochemical conversion technique that can transform wet biomass into energy and chemicals without pre-drying. So far, the process has yielded material that shows potential in facilitating the growth of non-edible crops, though Reza noted more testing needs to be done to see if the fertilizer could be used for growing food.
"The idea is human sewage has pathogens, and we have to kill and sterilize them," Reza said. "If we do high temperature, high pressure, many of these pharmaceuticals in the waste, such as antibiotics and active ingredients of birth control pills, will be degraded."
In addition to providing potential farming benefits, this renewable approach could help homeowners financially. Nearly 22 million American households (approximately 25 percent of the total) use septic tanks. In Ohio, more than one million homes rely on their own treatment facility, with the percentage of homes with septic systems even higher in the rural Appalachian areas. A study by the Athens City-County Health Department showed more than 25 percent of septic tanks in Ohio are not performing well or failing due to the lack of understanding of the necessity of maintenance and/or expensive cleaning. To provide the cleaning service, septage haulers can charge around $200–$500 to homeowners, depending on the size and complexity of the tank. This is quite a significant cost for the rural homeowners, who have median and mean annual household incomes of $24,326 and $48,628, respectively.
"The idea was instead of the homeowners who could be struggling to pay for the septage pumping fee, could we convert their burden into something valuable and locally useful. This way we could eliminate the septic tanking pumping fee, with someone coming, taking it and converting it to fertilizer and selling it to the local community," Reza said. "That was the motivation: can we take this liability from the homeowners and turn into a profitable business?"
This approach could be good news to waterways, as well. Septage is considered hazardous as it can transmit diseases and is rich in nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium which can lead to damaging nutrient runoff. Excess amounts of nutrients in rivers and other bodies of water can cause harmful algal blooms and disrupt the reproductive endocrinology of fish.
In addition to testing the fertilizer for edible crop use, researchers also plan to look at ways the septic tank waste removal system would be implemented. Reza noted an ideal situation would be to have a hydrothermal treatment plant near a wastewater facility, though in rural areas that may not always be feasible. One idea they have is a mobile unit that can pick up the waste, convert it to fertilizer and then move on to the next house.
Reza and the researchers are also conducting a related project in Ohio, funded by the Sugarbush Foundation, that focuses on "vector attraction reduction." It looks at whether treatment of sewage can reduce the number of flies and other insects. The next step is to design a pilot system and then request approval from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency.
Reza hopes the projects' focus on rural areas will lead to better renewable resource initiatives overall.
"If we develop each individual county and utilize their own resources, that is going to make their county sustainable, and resulting in a sustainable state," he said. "Instead of developing the cities, perhaps we could sustainably develop rural counties, which will make a massive impact on U.S. sustainability."
(Phys.org)

(VAN) FAO-led publication outlines structure and highlights agenda including new harmonized indicators and capacity building accessible to all.

(VAN) Energy group experts left after draft guidance on global warming plans ‘did not reflect the industry view’.

(VAN) Special Event in New York explores the causes, consequences and solutions to the 2021-2023 food price inflation.

(VAN) Ahead of Cop30, the Guardian will profile each of the top 10 emitters and their plans – good or bad – to tackle emissions.

(VAN) Scientists have detected pesticides in rivers, lakes and oceans worldwide. So what are these pesticides doing to the fish?

(VAN) Farmers’ organisations from across the European Union feel that the EU is undermining farmers throughout the Union and call for reason.

(VAN) Director-General urges bigger and deeper thinking to address youth employment challenge.