November 27, 2025 | 23:55 GMT +7
November 27, 2025 | 23:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
November 27, 2025 | 23:55 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
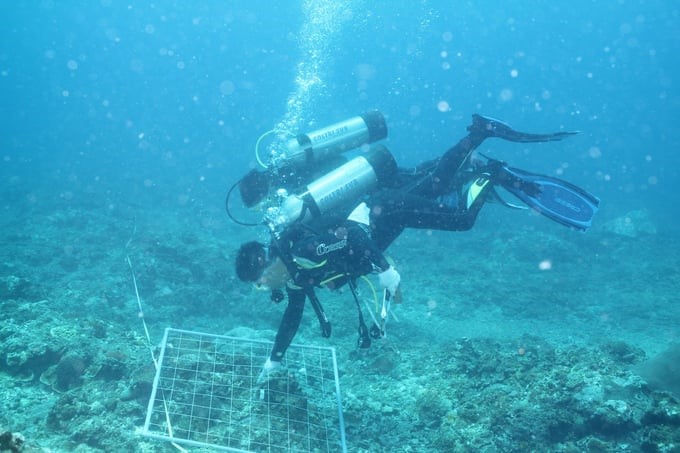

Scientists study seaweed species in the Gulf of Tonkin. Photo: RIMF.
Vietnam is located in the tropical monsoon region, with the length from North to South spanning over nearly 15 latitudes, so it has extremely rich and diverse marine creature resources. The territorial sea and exclusive economic zone are about 1 million km2 wide, with over 3,000 large and small islands stretching from North to South. The diversity of weather and climate conditions has created a very rich and diverse marine creature resource in Vietnamese waters.
In recent times, scientists from the Research Institute for Marine Fisheries (RIMF), the Institute of Marine Environment and Resources (IMER), and Nha Trang University have researched the species diversity and distribution of seaweed resources along 10 frontline islands representing ecological types from North to South in the Vietnamese waters.
As a result, the research process recorded 375 species of seaweed belonging to 62 families, 26 orders of 4 alga phyla. Among them, the Blue-green seaweed (Cyanophyta) has 16 species, the Red seaweed (Rhodophyta) has 193 species, the Brown seaweed (Phaeophyta) has 72 species, and the Green seaweed (Chlorophyta) has 94 species.
The initial step discovered four new seaweed species added to the Vietnamese seaweed list, yielding an average seaweed resource on 10 frontline islands of 1,456 ± 304 g/m2. The depth range of the concentrated distribution of seaweed resources is 1-6 m of water.
Distribution situation of seaweed species. Photo: RIMF.
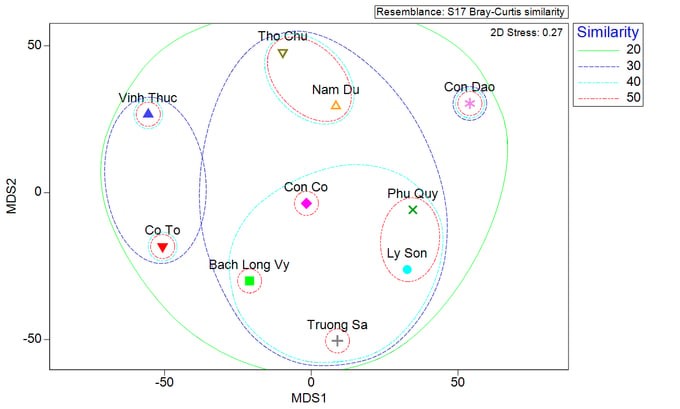
The frontline islands in the Central Coast region have a more diverse composition of seaweed species than the Northern and Southern regions. This diversity is closely related to geographical location, natural conditions, and the environment on each island.
To be more specific, the most diverse species composition was recorded in Ly Son with 143 species, followed by Phu Quy with 136 species recorded, Bach Long Vy with 112 species, three islands (Con Co, Con Dao, and Nam Du) also recording 96 species, Spratly Island with 81 species, Co To with 79 species, and Vinh Thuc with 70 species.
The lowest is Tho Chu Island, with only 69 species recorded. The depth range of the concentrated distribution of seaweed resources on the frontline islands is 1-6 m of water. The results of this study have provided an important scientific database for assessing the potential of seaweed resources along the frontline islands in Vietnamese waters.
The lowest is Tho Chu Island, with only 69 species recorded. The depth range of the concentrated distribution of seaweed resources on the frontline islands is 1-6 m of water. The results of this study have provided an important scientific database for assessing the potential of seaweed resources along the frontline islands in Vietnamese waters.
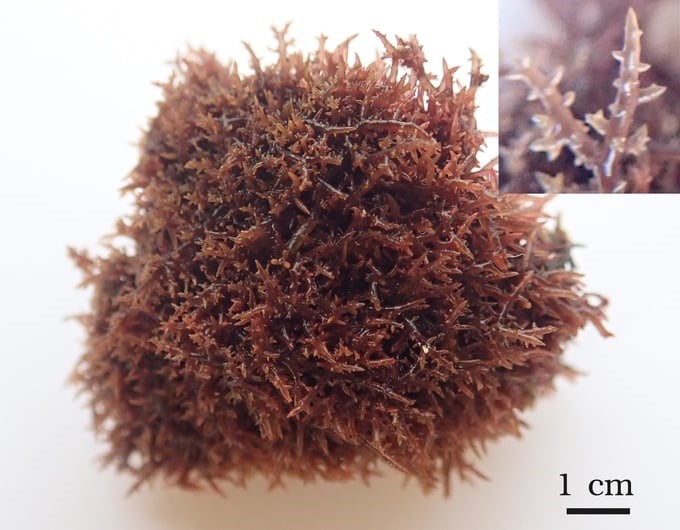

One of four newly discovered seaweed species. Photo: RIMF.
However, research on marine creature resources here is not much, especially research on seaweed resources in these areas, which is still scattered, not systematic, and has not been comprehensively researched during a certain time.
Dr. Do Anh Duy commented that the main reason for the above-mentioned situation is that these islands and archipelagos are located far from the mainland, transportation is difficult, and financial conditions are tight, leading to limitations on information about seaweed resources here.
Up to now, there have been a number of studies on seaweed resources on islands in the Vietnamese waters, but most of these are individual studies and have been researched for a long time, and information on the current resource status has not been updated.
Therefore, in order to gradually obtain information, build an overall picture of the current status of seaweed resources on the frontline islands, and update the Vietnamese seaweed list, research on species diversity and distribution of seaweed resources on these islands and archipelagos is necessary.
“This is the latest research result on seaweed resources along the frontline islands in Vietnamese waters. The results of this study provide an important scientific database for assessing the potential of seaweed resources along the frontline islands, contributing to affirming the national sovereignty over the sea and islands," Dr. Do Anh Duy shared.
Analysis results show that the coastal areas of the Central islands (Con Co, Ly Son, Spratly Island, Phu Quy) have the highest number of seaweed species (with 310 species, accounting for 82.7% of the total number of species); next is the area along the Southern islands (Con Dao, Nam Du, and Tho Chu) with 221 species, accounting for 58.9% of the total number of species. The lowest is the coastal waters of the islands in the Northern region (Vinh Thuc, Co To, and Bach Long Vy), with 218 species identified, accounting for 58.1% of the total number of species.
Translated by Huyen Vu Thu

(VAN) On November 27, in the meeting with Minister Tran Duc Thang, Mayor Yin Yong shared Beijing’s experience to improve environment and air quality.

(VAN) After 30 years, both sides identified strategic areas of cooperation: sustainable production, increasing coffee value and training for farmers.
/2025/11/27/4910-4-164708_294.jpg)
(VAN) On the afternoon of November 27 in Beijing, Minister of Agriculture and Environment Tran Duc Thang held a working session with several major Chinese enterprises operating in the agriculture and environment sector.

(VAN) The Department of Animal Health issued a provisional guideline requesting local authorities to increase surveillance, collect samples for testing, and conduct epidemiological investigations according to the established procedure.

(VAN) The United Nations recommends that Vietnam utilize data and artificial intelligence to enhance early disaster warnings and reduce GDP losses by 3.2% in the context of climate change.

(VAN) On the morning of November 27 in Beijing, Minister Tran Duc Thang and the Deputy Commissioner General of the General Administration of Customs of China signed a protocol on fresh jackfruit exports.

(VAN) As floodwaters recede, a vast network of irrigation works across eastern Gia Lai is emerging in a state of severe disrepair, with extensive damage demanding urgent restoration ahead of the 2025-2026 winter-spring cropping season.