November 28, 2025 | 01:27 GMT +7
November 28, 2025 | 01:27 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
November 28, 2025 | 01:27 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
The OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2023 forecasted that poultry would comprise 40% of global meat production that year, with a predicted increase from 142 million tonnes produced in 2023 to 153 million tonnes by 2030. Although welcome growth to the sector, it brings added pressure on producers and integrators to optimise efficiencies and boost productivity — while maintaining high standards of animal welfare throughout the production chain.
Modern poultry operations benefit from today’s advanced technologies, such as artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics, which can be utilised across various stages of production. Wherever they’re introduced, there can be transformative knock-on effects felt throughout the entire poultry value chain.
Although its adoption varies globally, chick sexing is a crucial step that can significantly boost the bottom line for producers, farmers, processors and integrators.
In more developed countries with advanced poultry industries, the practice is widely implemented, with producers looking for new automated methods that can enhance efficiency throughout the production process.
Separating males and females early on brings a whole host of benefits, including the ability to implement sex specific management and feeding practices that can reduce FCR, enhance predictability of days to achieve target weight, and improve weight uniformity at the plant.
In developing countries, the value of chick sexing is widely understood, and many poultry producers have implemented this practice. However, the primary challenge remains finding qualified labour to perform manual sexing, as automated technology has only recently become accessible.
Several methods are employed for chick sexing, each with its own benefits and limitations.
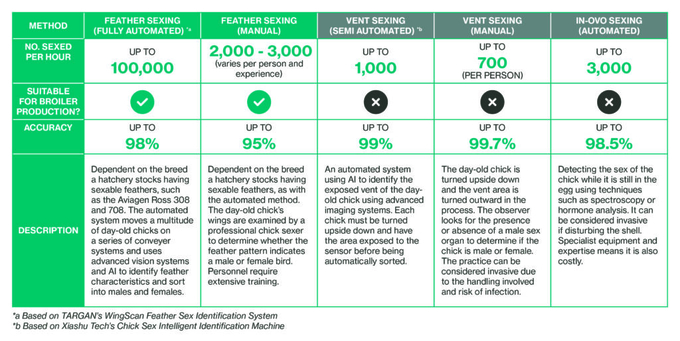
As illustrated above, automated imaging systems using AI are beginning to infiltrate the market due to the multitude of benefits across the broiler production value chain, including:
Efficiency: Reduced labour translates to a reduction in costs and minimised human error. Systems such as WingScan (TARGAN) allow larger quantities of chicks to be processed at standard mega hatchery throughputs, ensuring timely delivery to farms and markets.
Production: Feeding regimes and housing conditions can be tailored to the specific needs of male and female chicks, supporting overall health and productivity.
Welfare: Fully automated systems eliminate human interaction during the sexing process, reducing stress from handling and decreasing mixed-sex competition at farms.
Demand: Markets often prefer specific poultry products to meet consumer preferences and regulatory standards. Automated systems efficiently sex chicks, addressing increasing production demands and meeting market needs effectively.
Launched in 2023, TARGAN’s automated feather sex identification system utilises sophisticated vision systems to accurately identify day-old chicks. It transfers chicks on a series of conveyor belts and uses AI algorithms to sort males and females, with up to 98% accuracy. This translates into improved uniformity in bird weight on the farm and more efficient downstream processing, resulting in improved productivity, welfare and cost savings.
The WingScan system has processed millions of bird images, including various ages, producers, and incubation times, among many other factors. This extensive exposure allows its machine learning to continuously improve its AI algorithms through usage and expert review. Each WingScan system is meticulously designed to fit into existing hatchery setups and is intended to integrate into existing automation, positioned between shell separation and vaccination.
The future of the poultry industry lies in the hands of early adopters of advanced AgTech systems. By integrating engineering and biology, and embracing AI, poultry production is set to become more ethical, productive, and profitable. These innovations promise to transform the industry far beyond the hatchery, ensuring the rising global demand is met with quality animal protein products. Producers will benefit from increased efficiency and cost savings, consumers will enjoy high-quality products, and animals will experience improved welfare. This forward-looking approach positions the industry at the forefront of a new era in poultry production.
(Poultryworld)

(VAN) A new study reveals how the simultaneous effects of ocean acidification, salinity and loss of oxygen are making the world more fragile.

(VAN) Hopes are growing that the creation of the first 3D turkey gut model could be a turning point in the battle against the virulent blackhead disease.

(VAN) Tyson, America’s biggest meat supplier, plans to shutter one of its largest beef processing plants as the industry continues to struggle with low cattle supplies and political pressure from Washington.

(VAN) New FAO study shows how digital solutions are empowering farmers and fishers to prevent losses and build resilient agrifood systems.

(VAN) Brazil's COP30 presidency pushed through a compromise climate deal on Saturday that would boost finance for poor nations coping with global warming but that omitted any mention of the fossil fuels driving it.

(VAN) Poultry farmers in the UK have been warned that they could face one of the worst winters yet for bird flu.

(VAN) Prices of main-crop paddy have risen sharply, with jasmine rice hitting 16,100 baht per tonne — the highest level in years.