November 13, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
November 13, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
November 13, 2025 | 10:40 GMT +7
Hotline: 0913.378.918
The year 2025 marks the 80-year journey of Vietnam’s geology and mineral resources sector in accompanying the nation. Over eight decades, thousands of fundamental geological survey reports and mineral exploration studies have been completed, leading to the discovery and assessment of more than 5,000 mines and deposits of over 60 types of minerals.
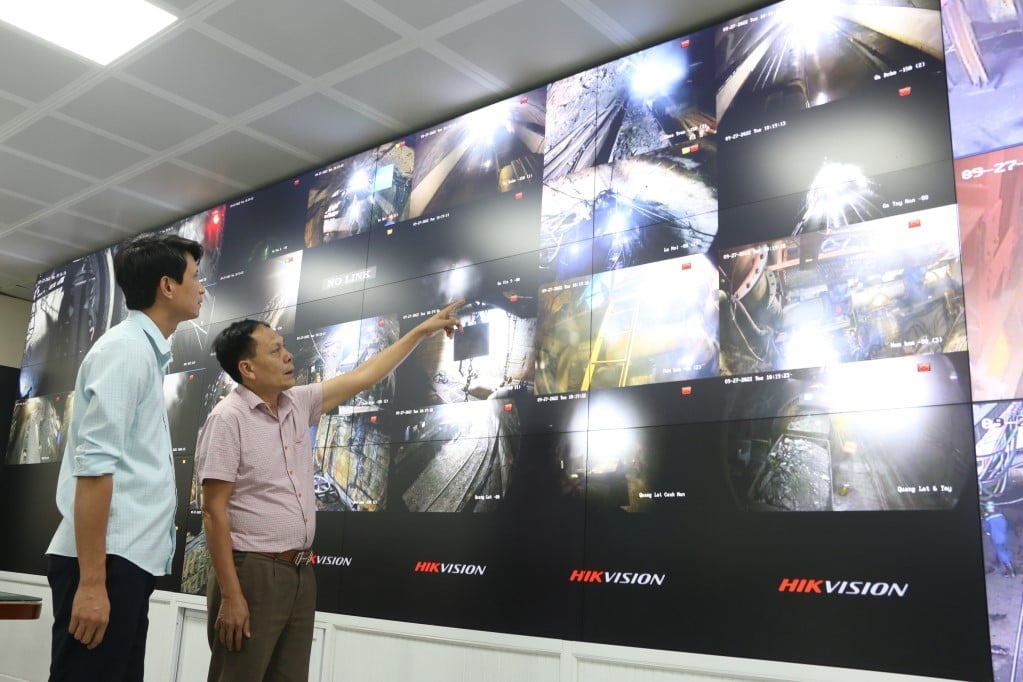

The centralized production control center of Mao Khe Coal Company integrates various modern information technology software applications into production management. Photo: Mai Anh.
Along with specialized geological maps at various scales, geological reports have built a vast and diverse system of geological information, data, and documents. This system has served multiple socio-economic sectors and supported the efficient exploitation of hundreds of mineral mines, meeting the country’s essential mineral material needs.
From the early days of handwritten field logs, hand-drawn geological maps, and paper archives, the sector has gradually shifted to applying modern technologies such as surveying, drilling, and sampling in the field, with data recorded directly into electronic logs and computers. In the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, digital transformation has become a global trend and an inevitable requirement across many fields, including geology and mineral resources.
Digital transformation at the source, applying digital technologies right from fundamental geological surveys and mineral investigations through to exploration, exploitation, and finally, mine closure data, plays a vital role in improving the management, protection, exploitation, and sustainable use of mineral resources.
One of the breakthroughs in geology and mineral resources legislation is the orientation toward building a comprehensive database covering the entire “geology–mineral resources journey.”
Accordingly, Article 89 of the 2024 Law on Geology and Mineral Resources clearly stipulates 14 categories of geological and mineral information and data that must be centrally and uniformly stored in the national database. These include data from fundamental geological surveys, mineral exploration surveys, geological environment monitoring, exploration reports, reserve approvals, as well as information on exploration and mining licenses, periodic reports - and ultimately, mine closure documentation.
Thus, upstream data (results from fundamental geological surveys) will be established and digitized at the highest level, forming the foundation to be supplemented by data from exploration, exploitation, and mine closure. By regulation, the national geology and mineral resources database is a unified collection of all geological survey results and mining activities nationwide, updated and managed consistently from central to local levels.
According to the Vietnam Mining Science and Technology Association, achieving this requires close coordination between state management agencies and enterprises to build a complete “digital profile” for each mine right from the initial stages of mineral survey and assessment. Completing the geology and mineral resources database at the source helps overcome past fragmentation and lack of consistency in data. Information is digitized under common standards, compatible with GIS systems, and integrated with cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), and big data analytics for more effective utilization.
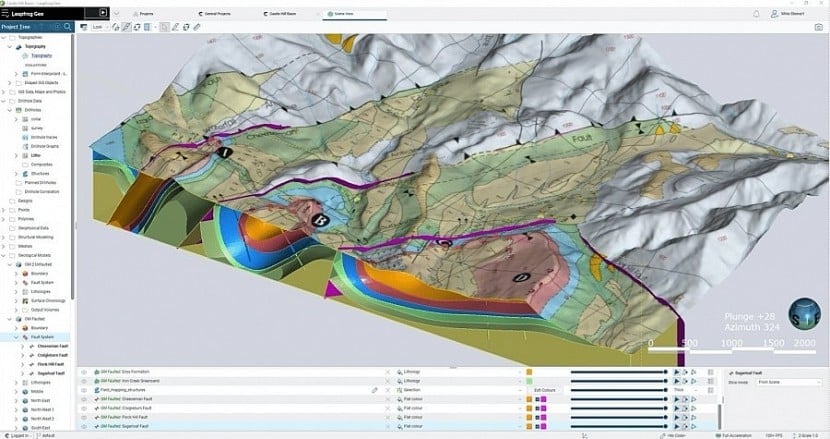
Application of 3D geological modeling technology. Photo: Leapfrog Geo software technology.
In particular, data from fundamental geological surveys, stored as “digital resources,” serve as a long-term foundation for building “digital datasets” throughout the entire process, from exploration and reserve approval to feasibility studies, investment decisions on mining, and ultimately, environmental rehabilitation and resource accounting at mine closure.
According to experts from the Vietnam Mining Science and Technology Association, the establishment of the national geology and mineral resources database and the regulations on digital transformation represent a continuation of the sector’s 80-year tradition. In the past, geological maps and mineral surveys laid the groundwork for the mining industry; today, “digital data” is set to propel the industry into a new era of modern governance.
When all geological survey data and exploration results are digitized, scientists and policymakers can easily access and utilize them. A unified geological and mineral database system will support the development of reports and visual maps for planning, monitoring, and research. At the same time, it allows this database to be linked with licensing and mining supervision information, enabling timely detection of violations and adjustment of mining plans as needed.
With interconnected data, the system can also generate 3D geological maps and apply AI technology to forecast the mineral resource potential of new areas.
To achieve these benefits, on the one hand, it is necessary to improve the legal framework and regulations on mineral data management and sharing. On the other hand, it requires investment in modern technological equipment as well as the development of a digitally skilled workforce. The Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment (now the Ministry of Agriculture and Environment), together with local authorities, has been promoting the development of a digital government architecture for the mineral resources sector, considering it a technical foundation for data integration.
Alongside these efforts, international cooperation projects on geological data digitization also contribute to the transfer of modern technology and data management expertise. At the same time, it is essential to develop a sectoral data architecture framework to standardize the storage, sharing, and security of information among stakeholders. Training and enhancing technological skills for staff is likewise a critical requirement for the successful implementation of digital transformation at the source.
Experts from the Vietnam Society of Mining Science and Technology emphasized that digital transformation at the source is not only about applying new and digital technologies, but also about a fundamental shift in processes and management mindset. This is regarded as a key strategy for developing the mineral sector in a sustainable, transparent, and efficient manner. Beyond strengthening the competitiveness of enterprises, digital transformation also contributes to optimizing resource use and minimizing environmental impacts.
Over its 80-year journey of development, the geology and mineral sector has affirmed its foundational role in socio-economic progress. In this “era of national rise,” the 2024 Law on Geology and Minerals and its implementing documents have paved the way to transform geological and mineral databases from a historical resource into a strategic “digital asset” for sustainable development.
Translated by Phuong Linh

(VAN) DLG President Hubertus Paetow affirmed that AGRITECHNICA 2025 will serve as the global hub for the future of sustainable agriculture.

(VAN) The Vietnamese delegation proposed three priority areas during the high-level segment of the 37th Meeting of the Parties to the Montreal Protocol (MOP 37) on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer.

(VAN) Looking back on the 80-year journey, also marking 80 years of the nation’s pursuit of Independence, Freedom, and Happiness, it is clear that agriculture and 'three rural issues', have always held a special place.

(VAN) The shared goal of Viet Nam and EU is to create a barrier-free cooperative environment that ensures balanced benefits and a common direction toward sustainable development.

(VAN) FAO Representative in Viet Nam stated that the country not only ensures domestic food security but also helps shape a sustainable global food system.

(VAN) Vietnam’s environmental sector affirms its pioneering role in protecting natural resources, maintaining ecological balance, and advancing sustainable, green, and harmonious national development.

(VAN) From straw, coffee husks, to sugarcane bagasse, agricultural by-products are being transformed into new resources for a lower-emission future in crop production.